Multivitamins: The World’s Go-To Health Boosters are a staple for many, promising a nutritional boost to support overall well-being. But are they truly a magic bullet? This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of multivitamins, exploring their benefits, potential drawbacks, and how to choose the right one for your unique needs. From understanding different types and ingredients to navigating potential interactions with other medications, we’ve got you covered.
We’ll unpack the science behind these supplements, examining research findings and exploring how multivitamins can impact various health conditions and demographics. Whether you’re a busy student, an athlete, or simply looking to optimize your nutrition, this guide provides actionable insights to make informed decisions about your health.
Introduction to Multivitamins

Source: bornfitness.com
Multivitamins are dietary supplements containing a combination of essential vitamins and minerals. They’re a popular choice for individuals aiming to fill potential nutritional gaps in their diet or boost overall health. While they can be beneficial, it’s crucial to understand their various forms, ingredients, and potential drawbacks before incorporating them into your routine. Remember, they’re not a replacement for a balanced diet, but rather a supportive tool.
Multivitamins come in diverse forms, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these variations helps you choose the best option for your needs and lifestyle. From convenient tablets to chewable gummies, the range of multivitamins caters to a wide spectrum of preferences and dietary requirements.
Common Types of Multivitamins
Multivitamins are available in various forms, catering to different preferences and needs. These include tablets, capsules, and gummies.
- Tablets are a common and often affordable option. They typically consist of compressed vitamin and mineral powders, and can be easily swallowed with water. They often require careful adherence to recommended dosage instructions.
- Capsules, often made of gelatin, house the vitamins and minerals within a soft or hard shell. This form allows for better absorption for some individuals, especially those with digestion issues. Capsules might offer a more convenient way to take higher doses of specific vitamins or minerals.
- Gummies are a popular choice, particularly for children and those who find swallowing tablets or capsules challenging. They are typically flavored and more palatable, making them easier to incorporate into a daily routine. However, they may contain added sugars or artificial flavors.
Typical Ingredients in Multivitamins
A typical multivitamin contains a blend of essential vitamins and minerals, varying by brand and formulation. Essential vitamins like vitamin A, C, D, and E, along with B vitamins (like B1, B2, B6, and B12) are often included. Minerals like calcium, iron, zinc, and magnesium are also frequently found in multivitamin formulations. These ingredients are carefully selected and combined to address common nutritional deficiencies.
Multivitamin Forms and Considerations
The table below Artikels different multivitamin forms, their pros, cons, and suitability for various demographics.
| Form | Pros | Cons | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tablets | Affordable, widely available, generally easy to swallow | Can be less palatable for some, potential for digestive issues in some individuals. | Suitable for most adults, especially those on a budget. Potential for interaction with certain medications |
| Capsules | Often better absorbed than tablets, potentially easier to swallow for some | Can be more expensive than tablets, may not be suitable for individuals with swallowing difficulties. | Suitable for adults and potentially suitable for those with digestive issues, or those requiring specific higher doses of vitamins/minerals |
| Gummies | Palatable, easy to consume, especially for children and those who dislike traditional forms | Often contain added sugars and artificial flavors, may not be as effective as tablets/capsules in delivering specific amounts of vitamins and minerals | Suitable for children and adults who find other forms unappealing. Not ideal for those on a low-sugar diet. |
Benefits of Multivitamin Use
Multivitamins have become a staple in many people’s health routines, promising a range of benefits. While they can’t replace a healthy diet, they can be a helpful tool for supplementing nutritional gaps and supporting overall well-being. However, it’s crucial to understand that individual needs and responses to multivitamins can vary significantly.
Understanding the potential benefits of multivitamins, alongside the role of a balanced diet, is key to maximizing their potential impact on health. This often involves consulting with healthcare professionals to tailor recommendations to specific circumstances.
Potential Health Benefits
Multivitamins can offer a variety of potential benefits, but their effectiveness depends on various factors. They can assist in filling nutritional gaps, supporting energy levels, and boosting the immune system. However, their impact is highly individualized.
- Improved Nutrient Intake: A well-rounded diet is ideal, but life circumstances often mean that certain vitamins and minerals are harder to obtain through food alone. Multivitamins can help address these gaps. For example, vegetarians may benefit from B12 supplements, while those with limited access to fresh produce might benefit from vitamin C and D supplements.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Certain vitamins and minerals, like B vitamins and iron, play crucial roles in energy production. If dietary intake is insufficient, a multivitamin can support sustained energy levels, preventing fatigue and boosting overall vitality. Someone who exercises regularly might benefit from a multivitamin with a higher concentration of B vitamins.
- Boosted Immune Function: Vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc are essential components of a healthy immune system. A multivitamin can support immune function, potentially reducing the risk of infections, particularly during times of stress or illness.
Variability Based on Individual Needs and Health Conditions
The effectiveness of multivitamins is not universal. Individual needs and health conditions significantly impact how the body utilizes and responds to these supplements.
- Dietary Restrictions: Individuals with specific dietary restrictions, like vegetarians or vegans, might benefit from multivitamins designed to address potential deficiencies in nutrients like vitamin B12 or iron. For example, a vegan diet may need a multivitamin containing B12.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can impact nutrient absorption or require specific nutritional support. A doctor can advise on appropriate multivitamin use for individuals with conditions such as celiac disease or inflammatory bowel disease, ensuring the supplement complements existing treatments.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: The nutritional needs of pregnant and lactating women are elevated. Multivitamins specifically formulated for these stages can provide crucial nutrients to support the health of both mother and child. Prenatal vitamins are a prime example of this, tailored to support the growing needs of a developing fetus.
Role of a Balanced Diet in Relation to Multivitamin Use
A balanced diet remains the cornerstone of good health. Multivitamins are not a substitute for a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
A balanced diet provides the body with a wide array of nutrients in their natural forms, optimizing absorption and utilization.
Multivitamins can act as a supplemental support when a balanced diet falls short. This means that a healthy diet should be the primary source of nutrients, and multivitamins should be considered a supplement, not a replacement.
Comparison of Multivitamin Types
Different multivitamin types are tailored to specific needs. A multivitamin for energy might emphasize B vitamins, while one for immune support might focus on vitamin C and zinc.
| Multivitamin Type | Focus | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Support | B Vitamins, Iron | Increased energy levels, reduced fatigue |
| Immune Support | Vitamin C, Zinc, Vitamin D | Stronger immune response, reduced illness |
| Women’s Health | Iron, Calcium, Folate | Support for reproductive health, bone health |
Potential Drawbacks and Risks
Multivitamins, while often touted as health boosters, aren’t a magic bullet. Like any supplement, they come with potential downsides that can range from mild discomfort to more serious health concerns. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions about incorporating multivitamins into your routine.
Potential Interactions with Medications
Multivitamins can interact with prescription and over-the-counter medications. Certain vitamins and minerals can interfere with the absorption or effectiveness of medications. For instance, some vitamins can reduce the effectiveness of blood thinners, while others can interact with medications used to treat heart conditions or diabetes. It’s vital to discuss any multivitamin use with your doctor or pharmacist before starting, especially if you are taking other medications. This preventative measure is critical to ensure the safety and efficacy of your current treatment plan.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before starting any new supplement regimen, including multivitamins, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. A doctor can assess your individual health needs and determine if a multivitamin is appropriate for you. They can also help identify any potential risks or interactions with existing medications. This personalized approach ensures the multivitamin aligns with your overall health goals and doesn’t pose any harm. This proactive step is crucial for a safe and beneficial supplement experience.
Potential Side Effects
While some people experience no side effects from multivitamins, others may experience various symptoms. The severity of these side effects can vary significantly.
| Side Effect | Severity Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | Mild | Feeling queasy or having an upset stomach. Can often be managed with smaller doses or adjusting the time of intake. |
| Headache | Mild to Moderate | A common side effect, usually subsiding within a short period. Potential causes can range from individual sensitivities to interactions with other substances. |
| Diarrhea | Mild to Moderate | Frequent bowel movements. This may indicate an intolerance to certain vitamins or minerals. |
| Stomach upset | Mild to Moderate | Abdominal discomfort, cramping, or bloating. Again, often manageable by adjusting the dosage or intake timing. |
| Skin rash | Mild to Moderate | An allergic reaction. Can manifest as itching, redness, or hives. Requires immediate medical attention if severe. |
| Kidney stones | Moderate to Severe | Formation of solid masses in the kidneys. Potentially serious, especially with high doses of certain vitamins or minerals. |
| Liver damage | Severe | Rare but possible side effect, particularly with excessive intake of certain vitamins. Requires immediate medical attention. |
Multivitamin Selection and Usage
Picking the perfect multivitamin can feel like navigating a vitamin jungle. But fear not, fellow health enthusiasts! This guide will equip you with the knowledge to choose a multivitamin that truly works for *you*, ensuring you’re getting the right nutrients without unnecessary extras. Understanding your needs and the different types available is key to maximizing your multivitamin’s potential.
Choosing the right multivitamin isn’t a one-size-fits-all affair. Your individual needs, lifestyle, and dietary habits play a crucial role in determining the ideal multivitamin for you. This section will detail the factors to consider and provide a step-by-step guide for selecting and using multivitamins effectively.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Multivitamin
Understanding your specific nutritional needs is paramount when selecting a multivitamin. Consider your diet, lifestyle, and any potential deficiencies or health conditions. For example, vegetarians might need a B12 supplement, while pregnant women may require higher doses of folic acid. Age also plays a role, with specific needs emerging during adolescence and older adulthood. Consult your doctor to gain personalized insight into your nutritional requirements.
Selecting a Multivitamin That Best Suits Individual Needs
A tailored approach is essential. Look for multivitamins that address your unique needs. If you’re a vegan, look for a vegan-friendly option that’s fortified with B12. Athletes might need a multivitamin with higher doses of specific nutrients like vitamin D and magnesium. Furthermore, consider the form of the vitamins. Some people prefer tablets, while others may find chewable or liquid options more convenient. Read the label carefully and compare different products based on their ingredients, dosage, and quality.
Proper Dosage and Timing of Multivitamin Intake
Following the recommended dosage is crucial for maximizing the benefits of multivitamins without causing any adverse effects. Always adhere to the dosage guidelines printed on the product label. Excessive intake can lead to negative health consequences, so be mindful of the quantities you consume. Ideally, take your multivitamin with a meal to aid digestion and absorption. Consistency is key; try to take your multivitamin at roughly the same time each day to establish a routine.
Step-by-Step Guide for Selecting and Using Multivitamins
This step-by-step approach will help you navigate the world of multivitamins effectively:
- Assess your nutritional needs: Consider your diet, lifestyle, and any potential deficiencies or health conditions. Consult with your doctor to gain personalized insights.
- Research different multivitamin options: Read product labels carefully, comparing ingredients, dosages, and quality. Look for reputable brands and check for certifications.
- Choose a multivitamin that aligns with your needs: Select a multivitamin that addresses your specific requirements, such as dietary restrictions or lifestyle factors. Consider the form (tablets, chewables, liquids).
- Follow the recommended dosage: Always adhere to the dosage instructions on the product label. Do not exceed the recommended intake.
- Establish a consistent intake schedule: Take your multivitamin at roughly the same time each day with a meal for optimal absorption.
- Monitor your health: Pay attention to any potential side effects. If you experience any unusual symptoms, consult your doctor immediately.
Scientific Evidence and Research
Multivitamins have been a staple in many people’s health routines, but the science behind their effectiveness is often debated. This section delves into the scientific evidence surrounding multivitamin use, examining the research that supports or refutes their benefits, and how these findings translate to real-world applications. Understanding the nuances of this research is crucial for making informed decisions about incorporating multivitamins into your health plan.
Summary of Scientific Studies on Multivitamin Benefits
Numerous studies have investigated the effects of multivitamins on various health outcomes. However, a consistent and robust body of evidence demonstrating significant overall benefits across the population remains elusive. While some studies show potential positive impacts, others find no significant effect, and in some cases, even potential risks.
Key Research Findings on Multivitamin Effectiveness
The effectiveness of multivitamins varies significantly depending on the specific population being studied, the type of multivitamin, and the health outcomes being assessed. Some studies have shown potential benefits in specific populations, such as older adults or those with dietary deficiencies, but overall findings are often inconclusive. It’s important to note that many studies have limitations, such as small sample sizes, short durations, or varying methodologies. This makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about the overall effectiveness of multivitamins.
Interpreting Research Results in Real-World Contexts
Interpreting research results about multivitamins requires careful consideration of the study design, sample characteristics, and the specific outcomes measured. For example, a study showing a positive effect on vitamin D levels in a group of elderly participants doesn’t necessarily translate to a similar benefit for a younger, healthier individual. Furthermore, the potential benefits of multivitamins may not outweigh the potential risks for everyone. Individual circumstances, including pre-existing health conditions, dietary habits, and lifestyle choices, play a crucial role in determining whether multivitamins are appropriate. It is vital to consult with a healthcare professional before making decisions about multivitamin use.
Table of Key Findings from Different Studies
| Study | Sample Size | Methodology | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example Study 1 (Vitamin D supplementation in older adults) | 500 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Improved bone density in the vitamin D group, but no significant effect on overall health outcomes. |
| Example Study 2 (Multivitamin use and cardiovascular health) | 1000 | Cohort study following participants for 5 years | No significant association between multivitamin use and reduced cardiovascular risk. |
| Example Study 3 (Multivitamin use and cancer risk) | 2000 | Meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials | Mixed results; some trials showed a slight increase in cancer risk, while others showed no significant effect. |
Note: This table presents hypothetical examples. Actual studies and their results vary widely. Always consult reliable sources for specific details and interpretations.
Multivitamins and Specific Health Conditions: Multivitamins: The World’s Go-To Health Boosters
Multivitamins aren’t just a one-size-fits-all solution for everyone. Their potential impact on specific health conditions varies significantly, and personalized approaches are crucial. Understanding how these supplements interact with pre-existing conditions is key to making informed decisions. While they can be a helpful tool, they shouldn’t replace a doctor’s advice.
A crucial aspect of using multivitamins effectively is recognizing their potential to either complement or exacerbate existing health issues. Some conditions may require specific nutrients to thrive, while others might be negatively affected by certain vitamin combinations. Consult a healthcare professional before incorporating multivitamins into your routine, especially if you have any underlying health concerns.
Impact on Specific Health Conditions
Multivitamins can play a supportive role in various health conditions, potentially aiding in symptom management and overall well-being. However, their efficacy and safety need to be assessed carefully for each individual.
Role in Supporting Various Health Conditions
Multivitamins can support conditions like anemia, by providing essential iron or B vitamins. In cases of weakened immunity, certain vitamin combinations can bolster the immune system. Individuals with digestive issues may benefit from targeted multivitamins to ensure adequate nutrient absorption. It’s important to note that these benefits are often best realized when coupled with a healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet.
Need for Personalized Recommendations
A personalized approach is paramount when considering multivitamins for specific health conditions. A doctor can assess individual needs, consider any existing medical conditions, and determine the optimal vitamin combinations. They can also advise on potential interactions with medications. This tailored approach is crucial to avoid adverse effects and maximize the benefits of multivitamin use.
Potential Multivitamin Benefits for Specific Conditions
| Health Condition | Potential Multivitamin Benefits | Important Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Anemia | Multivitamins containing iron, vitamin B12, and folate can help increase red blood cell production, alleviating symptoms like fatigue and weakness. | Consult a doctor to determine the appropriate dosage and type of iron supplement. |
| Weakened Immunity | Certain multivitamins, especially those with vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc, can support immune function and help the body fight off infections. | A healthy diet and lifestyle are equally important for a strong immune system. |
| Digestive Issues | Specific multivitamins with digestive enzymes or probiotics may help improve nutrient absorption and alleviate digestive discomfort. | Always consult a doctor before taking multivitamins with digestive support, as some ingredients may interact with certain medications or conditions. |
| Pregnancy | Prenatal vitamins are formulated to meet the increased nutrient needs of pregnant women, often including folic acid, iron, and calcium. | Prenatal vitamins should only be taken under the guidance of a doctor, and should not be substituted for a balanced diet. |
| Post-Surgery Recovery | Multivitamins can aid in the recovery process by replenishing essential nutrients lost during surgery or illness. | Consult with a doctor or registered dietitian to determine the most suitable multivitamin and dosage for post-surgical recovery. |
Multivitamins and Specific Demographics
Multivitamins are a popular supplement, but their effectiveness and suitability can vary significantly depending on individual needs. Different demographics, like children, pregnant women, and athletes, have unique nutritional requirements that may necessitate specific multivitamin formulations. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed choices. Tailoring multivitamin intake to specific needs can help optimize health and prevent deficiencies.
Individual nutritional needs are influenced by factors such as age, gender, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions. This makes a one-size-fits-all approach to multivitamin supplementation less effective. Recognizing these variations and adapting supplementation accordingly is essential for achieving optimal health outcomes.
Multivitamin Needs Across the Lifespan
Multivitamin needs evolve throughout life, reflecting changing nutritional requirements. Children, for instance, require specific nutrients for growth and development, while adults may have different needs based on age-related changes in metabolism. Pregnant women and athletes also have heightened nutritional demands.
Multivitamin Recommendations for Children
Children require a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients for healthy growth and development. Multivitamins can supplement dietary gaps, especially in picky eaters or children with specific dietary restrictions. Iron, vitamin D, and calcium are often highlighted as crucial for children’s development. A child’s multivitamin should ideally be tailored to their specific age and needs, with careful consideration of potential allergies or sensitivities.
Multivitamin Recommendations for Pregnant Women
Pregnancy presents unique nutritional challenges. Increased demands for certain nutrients, like folic acid, iron, and calcium, are essential for the developing fetus. Folic acid, for example, is crucial for preventing neural tube defects. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations on multivitamin supplementation during pregnancy.
Multivitamin Recommendations for Athletes
Athletes often have higher energy demands and specific nutrient needs. Multivitamins can help support energy production, muscle recovery, and overall performance. Electrolytes and antioxidants are often key components in sports multivitamins. However, athletes should consider their individual training intensity and dietary habits to determine the appropriate multivitamin intake.
Recommended Daily Intake Levels for Various Demographics
| Demographic | Nutrient | Recommended Daily Intake (approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| Children (ages 6-12) | Iron | 8-10 mg |
| Vitamin D | 600 IU | |
| Calcium | 1000-1300 mg | |
| Pregnant Women | Folic Acid | 400-800 mcg |
| Iron | 27 mg | |
| Calcium | 1000-1300 mg | |
| Adult Males | Vitamin C | 90 mg |
| Vitamin E | 15 mg | |
| Zinc | 11 mg | |
| Adult Females | Vitamin C | 75 mg |
| Vitamin E | 15 mg | |
| Iron | 18 mg |
Note: These are approximate values and may vary based on specific individual needs and conditions. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Multivitamins and Dietary Restrictions
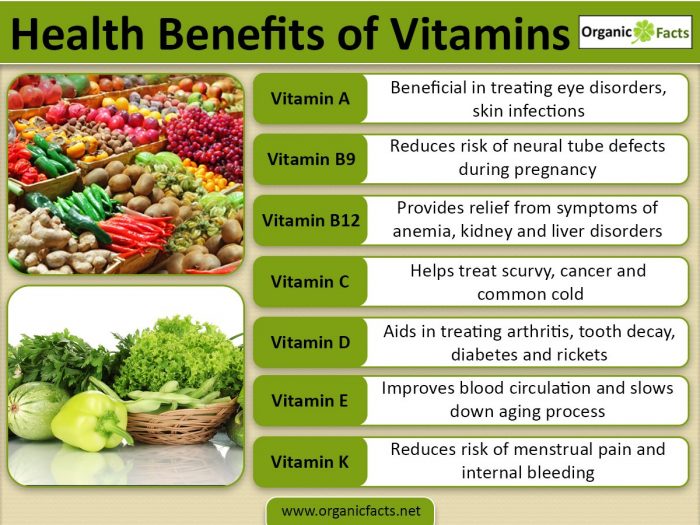
Source: organicfacts.net
Navigating dietary restrictions can be tricky, especially when it comes to getting all the essential nutrients. Luckily, multivitamins can be a fantastic tool for ensuring you hit your nutritional targets, even if you’re following a specific diet. They’re like personalized nutritional safety nets, offering a convenient way to address potential gaps in your intake.
Dietary restrictions often mean limiting certain food groups, potentially leading to deficiencies in specific vitamins and minerals. Multivitamins can bridge this gap by providing a concentrated dose of essential nutrients tailored to meet these needs. This is particularly helpful for vegetarians, vegans, and those following gluten-free diets. The key is finding a formula that aligns perfectly with your individual dietary choices.
Vegetarian and Vegan Multivitamins
Many multivitamin brands offer specialized formulas for vegetarians and vegans. These formulas typically avoid animal-derived ingredients like gelatin, ensuring they are suitable for those avoiding animal products. Crucially, they often emphasize plant-based sources of key nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and vitamin D, which are sometimes harder to obtain solely from a plant-based diet.
Gluten-Free Multivitamins, Multivitamins: The World’s Go-To Health Boosters
Gluten-free multivitamins are designed for individuals with celiac disease or those following a gluten-free diet. These formulations meticulously avoid gluten-containing ingredients like wheat, barley, and rye. This is vital for maintaining digestive health and preventing potential adverse reactions. Many gluten-free options are carefully formulated to avoid cross-contamination, ensuring complete adherence to the gluten-free principles.
Finding the Right Multivitamin for Your Dietary Needs
When selecting a multivitamin for a specific dietary restriction, it’s crucial to carefully examine the ingredients list. Look for products that explicitly state they are suitable for vegetarians, vegans, or gluten-free diets. Reading reviews from other consumers who have similar dietary needs can offer valuable insights into the product’s effectiveness and quality. Websites of reputable supplement brands or nutritional experts often provide further details on specific formulas and their suitability. Checking with a healthcare professional is always recommended before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
Examples of Suitable Multivitamins
Numerous multivitamin brands cater to diverse dietary needs. For vegetarians and vegans, look for options specifically marketed as “vegetarian” or “vegan.” For gluten-free needs, check product labels for the “gluten-free” certification. Specific examples include brands like [Example Brand 1] and [Example Brand 2], which often have product lines designed for various dietary restrictions. Be sure to compare different options to find the best fit for your individual needs and budget.
Multivitamins and Supplements
Stepping into the world of health supplements can feel like navigating a complex maze. From multivitamins to specialized formulas, understanding the differences and potential interactions is key to harnessing their benefits safely. This exploration dives into the nuances of these often-overlapping worlds, offering insights to empower informed choices.
Multivitamins are essentially a combination of essential vitamins and minerals, designed to address potential deficiencies. Other supplements, on the other hand, can range from single nutrients to herbal extracts, targeting specific health concerns or enhancing certain bodily functions. While multivitamins aim for general well-being, other supplements often focus on more targeted improvements.
Distinguishing Multivitamins from Other Supplements
Multivitamins offer a balanced blend of nutrients, attempting to address potential gaps in a person’s diet. Other supplements, in contrast, often focus on a singular nutrient, herb, or compound. This difference in scope reflects the varied needs and objectives they aim to fulfill. For instance, a vitamin D supplement addresses a specific vitamin deficiency, whereas a multivitamin aims to cover a wider spectrum of nutritional requirements.
Comparing Benefits and Drawbacks
Multivitamins are often beneficial for individuals with dietary restrictions or those who struggle to obtain adequate nutrients through their diets. They can help bridge nutritional gaps and potentially prevent deficiencies. However, multivitamins may not always be necessary for those with balanced diets. Other supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, may offer specific health advantages, like improved heart health. However, they may also come with potential side effects or interactions, and often require a doctor’s guidance.
| Feature | Multivitamins | Other Supplements |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Broad, covering multiple nutrients | Targeted, focusing on a specific nutrient or compound |
| Potential Benefits | Improved overall nutrition, preventing deficiencies | Addressing specific health concerns, enhancing specific bodily functions |
| Potential Drawbacks | Possible unnecessary intake of certain nutrients, potential for interactions | Potential side effects, interactions with medications, need for professional guidance |
Potential Interactions
Multivitamins and other supplements can interact, potentially enhancing or diminishing the effects of each other. For example, certain minerals, like calcium and iron, can interfere with the absorption of each other if taken together. Furthermore, some supplements may interact with medications, potentially leading to adverse effects.
Avoiding Harmful Interactions
Consulting a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen is crucial. This allows for personalized guidance based on individual health conditions and medications. A doctor can assess potential interactions and recommend appropriate dosages and timing. Furthermore, meticulously following recommended dosage instructions and staying informed about possible interactions is paramount. For instance, always inform your doctor about all supplements you are taking, including multivitamins. This will help them assess potential risks and ensure the supplements are safe and beneficial for your overall health.
“Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.”
Closing Notes
So, are multivitamins the miracle cure-all they’re hyped up to be? The truth is, while they can be a helpful tool, they’re not a replacement for a balanced diet. This guide has shown you the ins and outs of multivitamins, empowering you to decide if they’re the right fit for your health journey. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized recommendations, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking other medications. Ultimately, a holistic approach that combines a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and informed supplement choices is key to overall well-being.